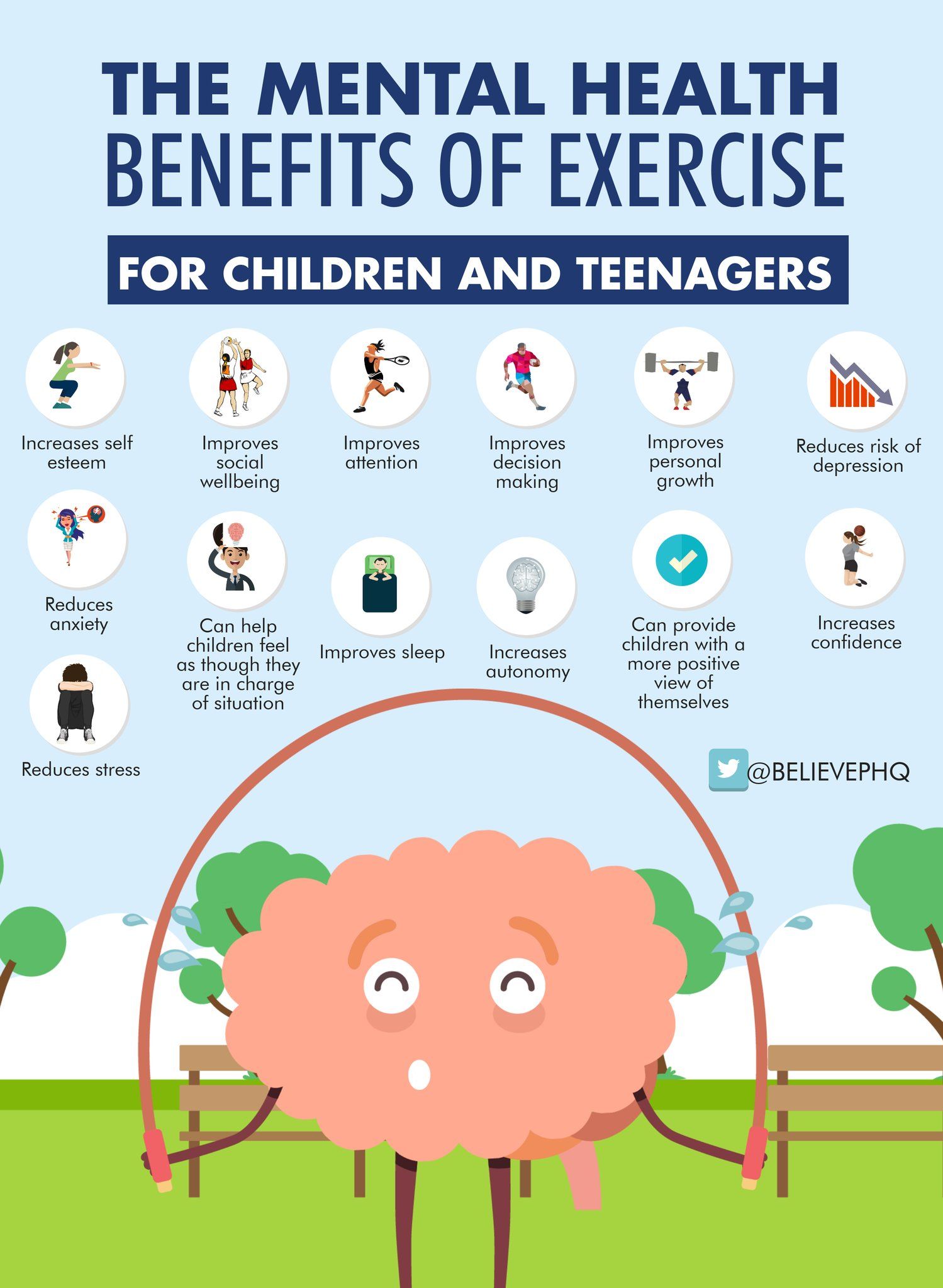
This article explores the deeply influencing role of habitual exercise for mental health. In general, it details how the act of exercising can also work as an antidepressive agent, as a tension reducer, and as mood-altering behavior that might contribute to the better working of cognition and enhancement of the emotional well-being of one. It goes further by considering the more substantial mechanisms of action for exercise from the release of neurotransmitters up to structural and hormonal brain changes. It then lists different benefits that exercise has on mental health, such as the reduction of anxiety, depression, and stress, improvement of sleep quality, and building self-esteem. Common questions about exercise and mental health are also addressed with practical recommendations and tips on how to include physical activity into daily life.

Reduce Stress & Anxiety
Stress and anxiety are major issues of modern life, characterizing much of the physical and mental stress there is. Exercise is an effective releaser for stress as well as an anxiety reducer through physiological changes that bring about relaxation and calm.
Release endorphins: Endorphins are natural mood-boosting chemicals released during exercise that give users feelings of euphoria and wellness.
Reduces cortisol concentration: Exercise reduces the stress hormone cortisol and results in a composure that reduces the manifestation of anxiety symptoms.
Work as an alternative source for distraction: Exercise distracted your mind from your worrisome mind and problems that were time passers temporarily evading the situation of anxiety.
Promote relaxation: Yoga and tai chi can ease out body tension, which works to promote relaxation while reducing the level of anxiety.
Anti-Depressant
Exercise has an enormous effect on depression, acting as a natural antidepressant that induces positive mood changes.
Raises serotonin: Exercise raises the levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation and happiness.
Stimulates neurogenesis: Physical activity stimulates the growth of new brain cells in the hippocampus, which is an important part of the brain involved in mood regulation.
Improves Sleep: Exercise regulates sleep patterns and helps sleep, which is one of the major management when it comes to managing the depression.
Increases Energy Levels: Exercise battles one of the very common symptoms of depression which is fatigue, bringing higher energy levels and hence high motivation.
Cognitive Function
Exercise isn’t just good for your body; it also has a positive impact on your mind. It can sharpen cognitive abilities, improve memory, and promote overall brain health.\
Increases blood flow: Exercise boosts blood flow to the brain, thereby supplying oxygen and nutrients to ensure perfect functioning of the brain.
Increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF): BDNF is the protein that helps in developing, surviving, and transmitting signals in brain cells. Exercise increases BDNF levels, thereby improving function in the brain.
It improves memory and learning: It has been found out that exercise benefits memory, attention, and learning functions in older adults
Cognitive decline prevention: Through exercise, one can be prevented from age-related cognitive decline and reduces the risks of demen
Quality of Sleep
Regular exercise may be effective in improving sleep quality, with enhanced restful sleep and reduced instances of insomnia.
Regulation of the circadian rhythm: Exercise works as a helping hand to enable your body to manage its normal sleep-wake cycle with a regular schedule.
Reduces stress and anxiety: Exercise helps one to reduce stress and anxiety, which causes sleep disorders most of the time.
Increases physical fatigue: You get physically fatigued, and you can fall asleep easily and sleep through the night.
Improves sleep efficiency: Exercise helps improve the sleep efficiency of a person; you spend more time in deep sleep and less in tossing and turning.
Boosting Self-Esteem
Exercise boosts self-esteem and self-confidence.
Feel of achievement: You’ll feel accomplished and build your self-confidence through working out.
Changes in physical appearance: Exercise changes the way you look, such as from weight loss to more muscle mass that enhances body image and confidence.
Increased energy: You feel energetic after exercising, so you are able to take on new challenges and pursue your goals with renewed confidence.
Increased mental endurance: Workout helps improve mental resilience, meaning a better chance of coping up with the stress and adversity that can come one’s way.
Benefits on mental health abound for regular exercise: it reduces the levels of stress and anxiety, fights depression, and improves cognitive functioning, besides generally making you feel healthy and well. By clearing some space in your busy schedule for exercise, you will begin to reap rewards from a healthier mind and body. Anything counts as a form of exercise, and what matters most is to find something enjoyable that becomes an ingrained habit.